新闻文章
启迈QIMA 2025年供应链信号报告:美国关税将全球供应链推向未知领域
[下载PDF版本]
启迈QIMA 供应链信号报告为您提供关乎全球贸易与采购格局的关键情报。本报告解读宏观及行业层面的趋势,为品牌和零售商提供来自启迈QIMA一线专家的可行洞察,助其预判新出现的供应链风险与机遇。
执行摘要
2025年上半年全球贸易与采购态势
贸易不确定性达历史高位,美国关税击碎年初乐观情绪
欧洲展现经济韧性,制造业与消费者信心逐步复苏
供应链在动荡贸易环境中航行,采购与运输中断风险加剧
关键消费品行业面临加速多元化的压力
品牌与零售商对可持续性、可追溯性与循环性的要求日益提高
供应链研究员视角
"尽管全球贸易格局因美国关税及实际与感知的威胁而发生变化,美国经济在2025年上半年仍展现出显著韧性。供应链提供商正密切关注事态发展,国际货运量可能因此下降,而旨在减少关税风险的近岸外包举措则有望加速推进。" — Cathy Morrow Roberson,供应链撰稿人与研究员
全球贸易格局
消费品贸易:前景受不确定性拖累
在经历了富有韧性的第一季度后,全球贸易前景自4月起因一系列政策急转而遭受重创。中东局势的最新升级更为市场增添了新的波动性。在贸易不确定性处于历史高位之际,最新预测认为,随着制造商和投资者优先考虑风险规避,2025年全球货物贸易将出现萎缩。
启迈QIMA 2025年上半年的检验与审核数据凸显了关税紧张局势对全球供应链的影响,国际采购在第二季度急剧放缓,美国买家尤为明显。然而,东南亚却成为一个亮点,来自美国、欧盟和南美的制造业需求呈现强劲增长。
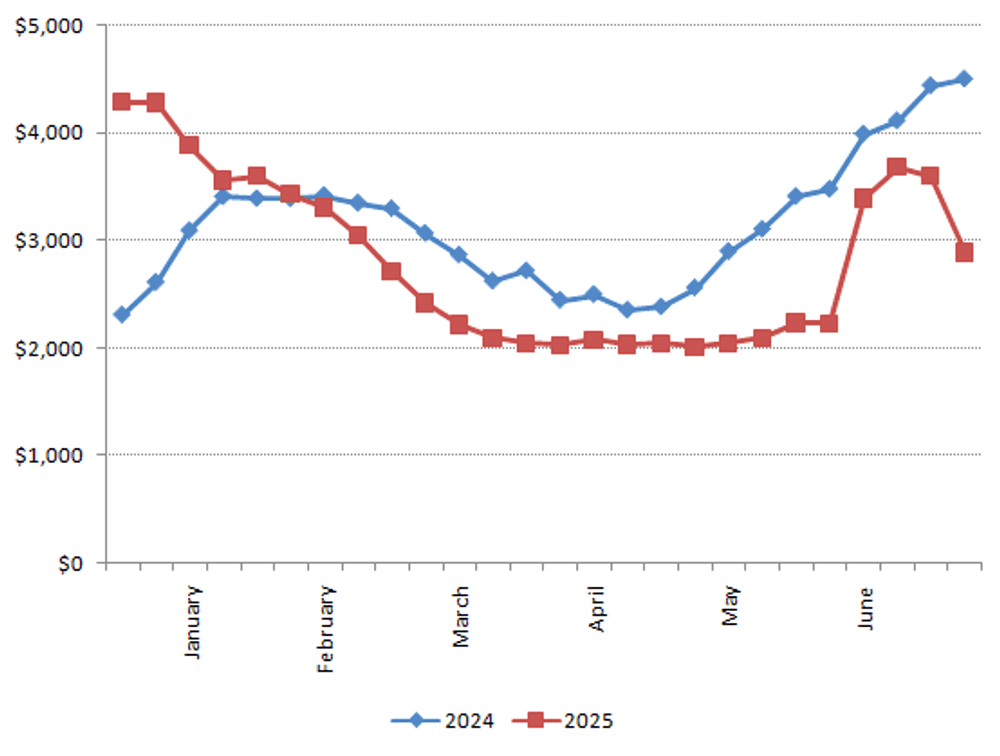
航运:2025年第三季度可能出现中断
整个2025年上半年,海运运价持续反映需求波动:从第一季度买家在美国关税生效前对中国进口商品完成提前备货后的暴跌,到6月份因90天关税暂停而引发的需求激增导致的运价飙升。
随着贸易紧张局势持续,需求的快速转变可能导致跨大西洋航线进一步的供应链中断。与此同时,欧洲供应链可能易受中东冲突引发的干扰影响。
波罗的海货运指数(Freightos Baltic Index)——全球(2025年上半年 vs 2024年上半年)
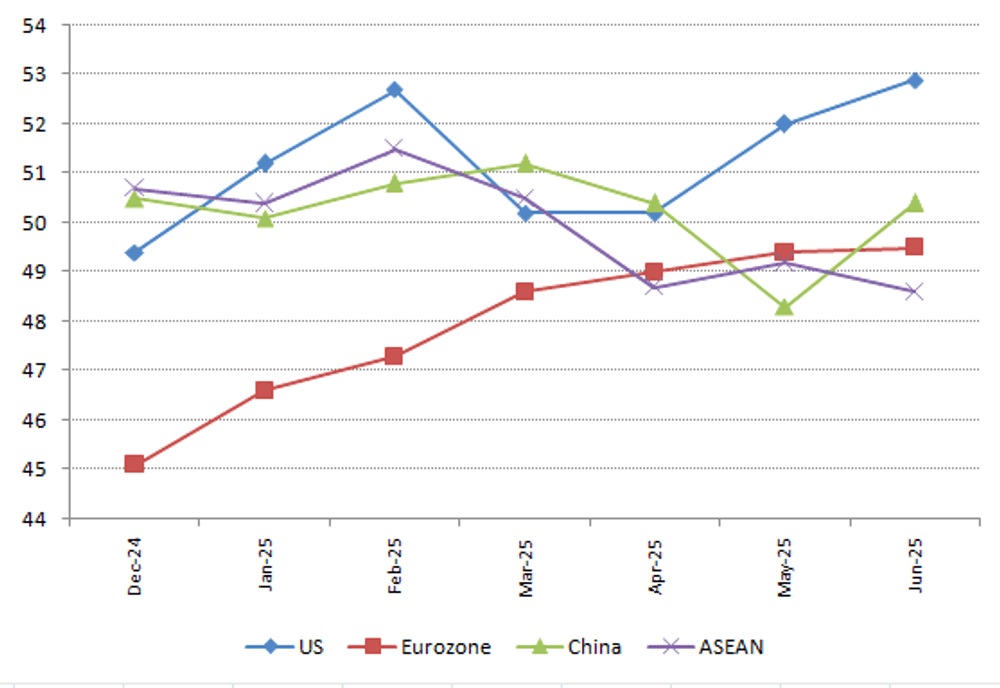
制造业:欧洲复苏,美亚承压
尽管年初存在乐观情绪及关税带来的暂时提振,2025年上半年美国制造业仍面临通胀和需求疲软的阻力。 受出口下滑和关税不确定性的影响,中国和东盟国家的增长势头受抑。相比之下,欧元区的采购经理人指数趋势指向持续复苏,所有四个主要欧元区经济体的生产均在回升。
主要产地区制造业PMI趋势:2025年上半年
经济展望:增长较去年放缓
在不确定性加剧的背景下,全球经济增长预计将较去年放缓,尤其依赖出口的新兴市场更为脆弱。然而,若主要经济体能就当前贸易争端达成持久解决方案,前景则有望改善。
消费者信心与购买行为
通胀压力缓解或难持久
2025年上半年,美国和欧元区的消费者价格通胀率持续下降,分别稳定在2.4%和2%左右。相比之下,由于需求疲软及国内零售商之间的"价格战",中国自2月份以来一直面临温和的通缩。 然而,持续的贸易紧张局势给未来数月带来了新的通胀风险,因为更高的关税可能推高消费者价格并抑制国际贸易。亚太地区经济体因其高度贸易开放性和对美国需求的依赖,尤其易受此类通胀压力影响。
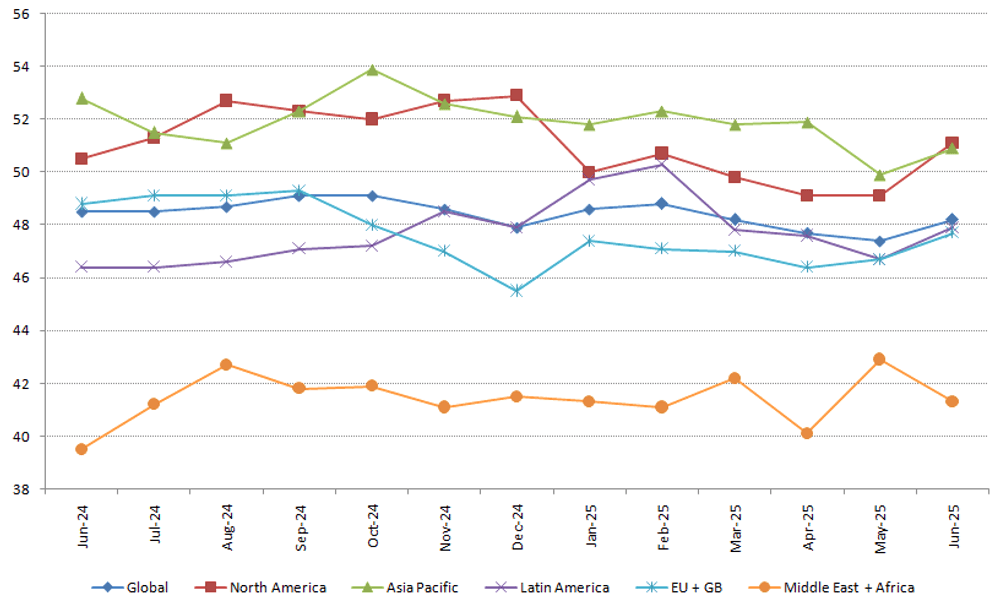
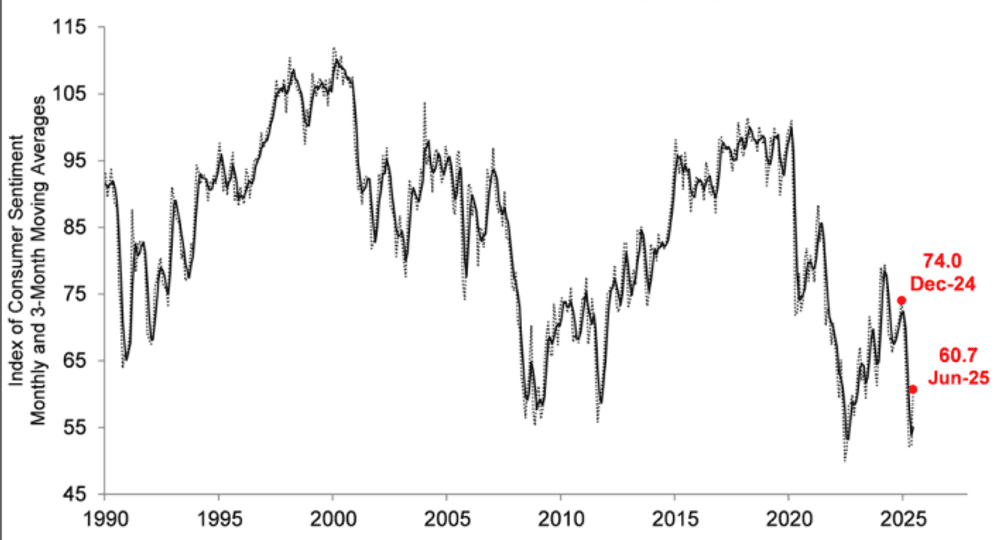
贸易政策影响消费者信心
2025年上半年,对经济前景持续的不确定性使消费者信心保持低迷,但6月份的小幅回升显示出乐观情绪有所回归。尽管在90天关税暂停宣布后,美国消费者信心在5月份曾短暂反弹,但受对关税和贸易政策的担忧影响,整体趋势向下,且受影响显著。
益普索全球消费者信心指数(Ipsos Global Consumer Confidence Index)
美国消费者信心指数(密歇根大学)(U.S. Consumer Confidence Index - University of Michigan)
Spending trends: good value is king
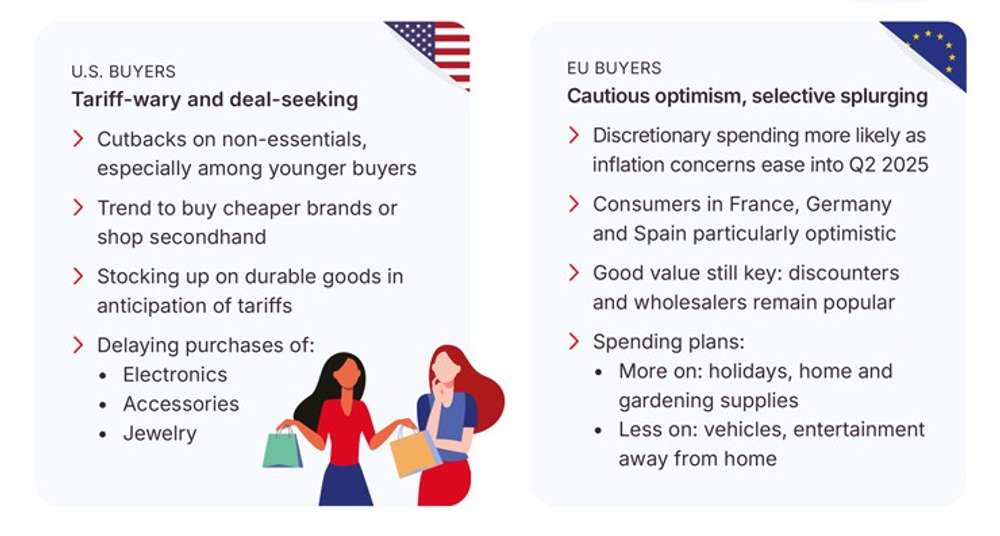
资料来源:Trading Economics, The Conference Board, McKinsey, University of Michigan, Investment Executive
行业深度聚焦:纺织、服装与鞋类
供应链现状:2025年上半年
全球纺织、服装和鞋类行业正努力应对美国贸易政策举措导致的生产中断、物流障碍和成本上升,同时面临日益增长的合规压力。
挑战
美国关税带来的运营冲击
美国关税引发的供应链冲击正在扰乱主要供应地区出口导向型的纺织服装产业,导致:
新兴经济体增长受抑
商业和消费者信心受挫
全球买家的采购环境稳定性下降
利润压力
Fash时尚消费者对价格越来越敏感,服装是经济下行时期消费者削减开支的主要类别之一。对品牌而言,这通常意味着不得不自行吸收因关税和供应链中断产生的大部分额外成本。
不断演变的合规环境
尽管美国和欧盟在部分可持续发展法规上有所延迟或倒退,但时尚品牌仍面临跟上一系列供应链和产品法规的压力:
安全性: 欧盟的《通用产品安全法规》已生效,对服务于欧盟市场的所有企业(包括直销和在线市场)施加了安全性与可追溯性义务。
循环性: 针对服装产业的"延伸生产者责任"计划正在欧盟和加利福尼亚州推行,预计更多司法管辖区将跟进。
可追溯性: 欧盟的"数字产品护照"规则将要求对在欧盟市场销售的所有服装产品,追溯并披露其原料来源、化学成分和环境足迹。
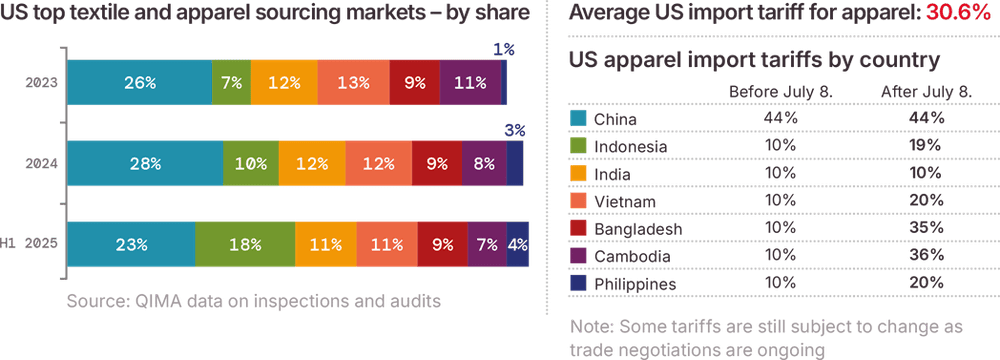
美国纺织服装进口受关税影响的程度
行业深度聚焦:玩具与休闲用品
供应链现状:2025年上半年
受美国关税影响,全球玩具供应链正面临严重干扰,中小企业受到的影响尤为强烈。专家预计,该行业从以中国为主导转向"多中心"模式的进程将坎坷不平,中国生产枢纽在过去数十年积累的专业制造知识及研发能力可能在此过程中流失。
多元化游戏:选择你的玩家

行业深度剖析:电器和消费电子产品
挑战
遵守可持续发展标准的压力
自 2025 年 6 月起,欧盟新的生态设计和能源标签规则将适用于在欧盟市场销售的智能手机、无绳电话和平板电脑,要求:
更高的产品和电池耐用性
及时供应关键备件,并确保在产品停产后仍能持续供应
更长时间的操作系统更新
标签上需包含能效、电池寿命、抗特定类型损坏能力以及可维修性评分等信息
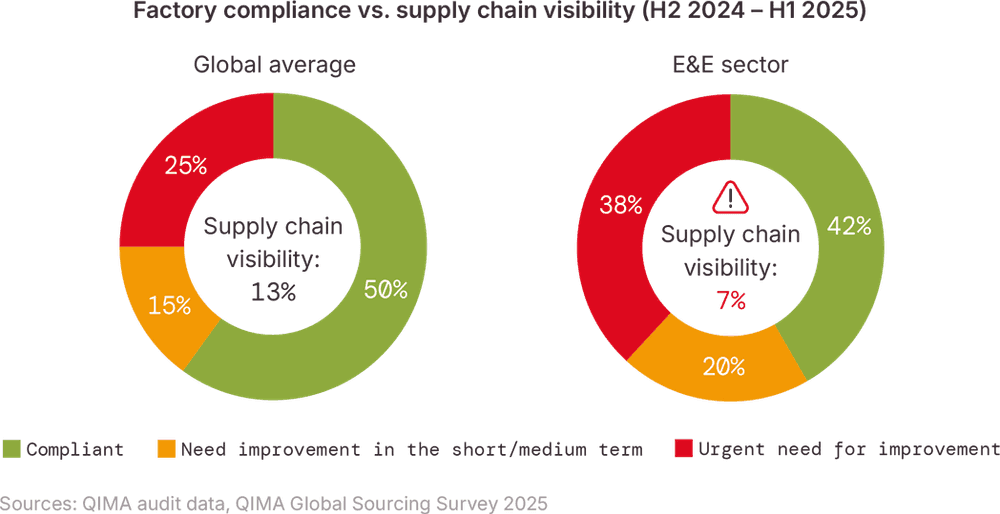
供应链不透明与人权风险 电子行业强迫劳动风险依然居高不下,供应链缺乏透明度是主要原因之一。在近期一份备受瞩目的基准报告中,科技行业在应对供应链人权风险方面的平均得分仅为20/100。此外,另一份报告指出,全球电池市场75%的份额都存在强迫劳动和童工风险。
QIMA 的数据凸显了电子电气行业供应链不透明与人权风险增加之间的联系:该行业的企业报告的供应链透明度低于其他行业,同时,电子电气产品制造工厂的严重违规行为也明显更为频繁。
启迈QIMA 如何助力降低风险
风险映射与缓解方案
启迈QIMA 结合实时全球预警、ESG 风险映射以及实地考察和审核,帮助品牌将风险转化为韧性。 借助 QIMA Risk Radar 等供应链风险映射与缓解方案,企业可以预测中断风险,确保合规性,并构建更透明、更可持续的供应链,从而在日益复杂的采购环境中保持领先地位。